In the world of investment and financial trading, mastering and applying effective tools is key to an investor’s success. Among these tools, ‘Trailing Stop’ is a concept that cannot be overlooked. This article will provide you with an in-depth look at Trailing Stop – a smart risk management strategy, helping you optimize profits and minimize losses in trading. Whether you are a beginner or experienced, the following detailed and easy-to-understand information will help you better understand Trailing Stop and how to apply it effectively in your investment activities. Let’s explore together!
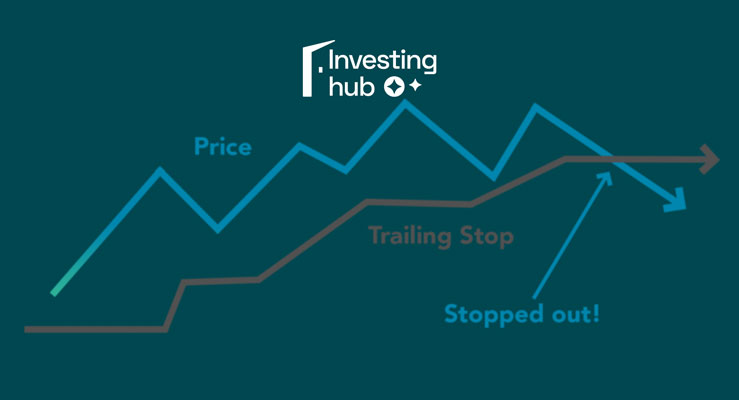
What is a Trailing Stop?
Trailing stop is a term familiar to those in the financial trading markets, especially at connextfx.com. Simply put, a trailing stop is a type of flexible stop-loss order that automatically adjusts to market prices. Its unique feature is the ability to adjust automatically, allowing investors to “follow” profits without needing continuous operations.
For example, suppose you buy a stock at $100 and set a trailing stop of 5%. If the stock price rises to $110, then the trailing stop will also “climb” to $104.5 ($110 minus 5%). It will only activate if the stock price falls below $104.5. This facilitates the optimization of profit while minimizing the risk of loss.
However, remember that trailing stops are not magical. They cannot protect you from all risks, especially in highly volatile markets. Nevertheless, they are a powerful tool, helping investors be more proactive in risk management and profit preservation. Therefore, use it smartly and flexibly!
Why Use a Trailing Stop
First and foremost, trailing stops protect profits. As the price of stocks or assets rises, the trailing stop moves along, allowing investors to retain most of the profit if prices start to decline. This means you don’t have to constantly monitor the market.
Secondly, trailing stops also minimize risks. They automatically close trades when prices move in the opposite direction of expectation, limiting losses. This is particularly important in volatile markets, where every minute can lead to significant losses.
Finally, trailing stops allow for flexible trading. You don’t have to set a fixed stop loss. Instead, it adjusts automatically according to market movements, allowing you to “sleep well” without worrying about unforeseen fluctuations.
In summary, using a trailing stop is a smart strategy that helps you maximize profits and minimize risks. That’s why I always encourage investors, whether new or experienced, to actively use this tool in their investment strategy.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Trailing Stops
The advantages and disadvantages of trailing stops are two sides of the same coin in financial trading. Starting with the advantages, trailing stops are an excellent tool for preserving profits. As prices move in your favor, trailing stops also move, ensuring that you don’t miss out on profits from positive market fluctuations. It’s like having a guard always watching your back, ensuring your interests are safe.
But trailing stops are not always perfect. A significant disadvantage is that in fast and volatile markets, trailing stops may not reflect in time, leading to closing trades at an undesired level. Sometimes, temporary fluctuations can trigger trailing stops, causing you to miss recovery opportunities if prices turn positive again.
Another point to note is that trailing stops are not always suitable for every trading strategy. For investors who are high-risk takers or expect significant profits in a short time, using trailing stops can limit their ability to maximize profits.
In conclusion, while trailing stops are useful tools, they also have their limitations. I always advise investors to consider carefully when using this tool, combining it with other strategies for the best results in financial trading.
How Trailing Stop Orders Work
The operation of trailing stop orders is quite interesting, and I want to share this with you. Firstly, a trailing stop, also known as a moving stop-loss order, works based on setting a certain distance (percentage or specific amount) from the current market price of the investment asset.
For example, if you buy a stock at $100 and set a trailing stop of 5%, and the stock price rises to $120, the trailing stop will automatically adjust, maintaining a 5% gap from the new price, i.e., at $114. This means if the stock price falls below $114, the sell order will be triggered.
The key point here is that the trailing stop moves in the positive direction of the market but does not move in a negative direction. When the stock price increases, the trailing stop also increases, but if the price decreases, it remains stationary. This ensures that you can preserve profits when prices rise, and limit losses when prices fall.
In summary, trailing stops are a useful tool, allowing you to manage risk and profit flexibly. They let you “adjust” your stop-loss orders according to market movements.
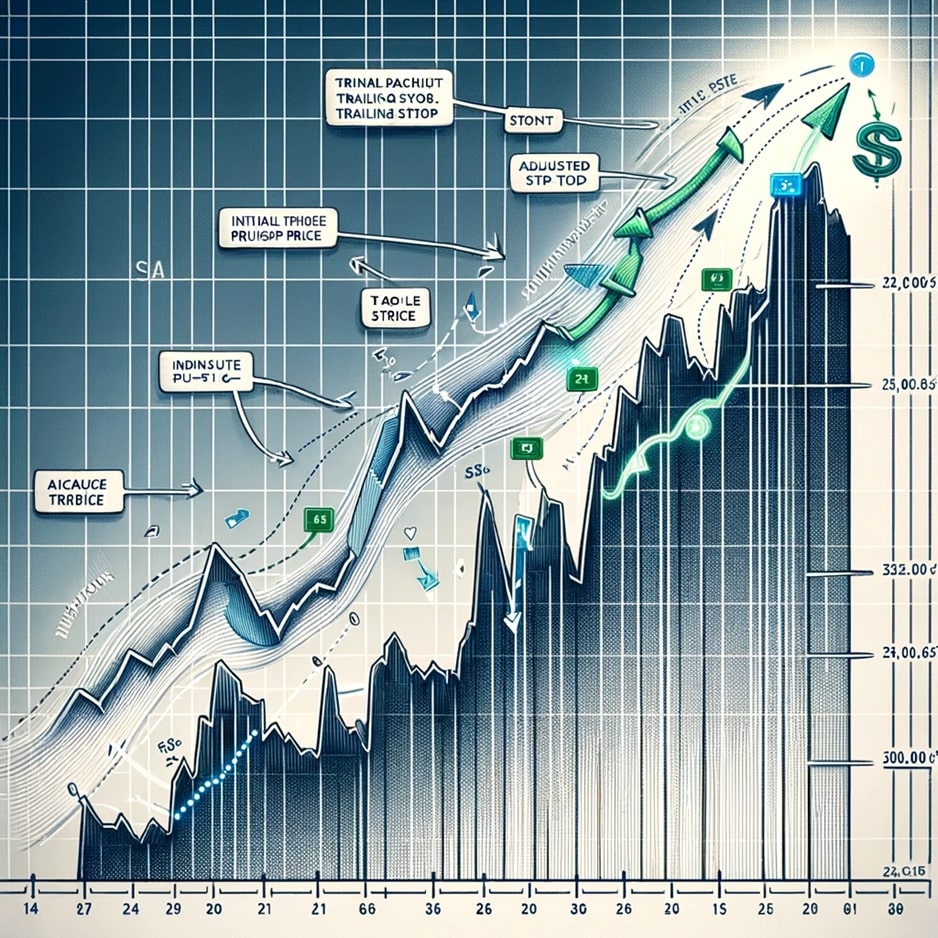
In the image above, you can see a detailed illustration of the concept of a trailing stop in stock trading. The stock price graph shows an upward trend, and along with it, the trailing stop line automatically adjusts upwards as well. The trailing stop line is represented in a distinct color, making it easy to distinguish its movement compared to the stock price. Annotations and labels in the image indicate important points such as the initial purchase price, the adjusted trailing stop price, and the point where the trailing stop will be triggered if the stock price begins to decline. This image is designed to be educational and easily understandable for those learning about stock trading concepts.
How to Set a Trailing Stop Order?
Setting a trailing stop order is not difficult, but it requires a basic understanding of how it works. First, you need to determine the trailing stop level that you want to apply. This can be calculated as a percentage or a fixed amount relative to the purchase price. For example, if you buy a stock at $100 and want to limit your risk to 5%, you would set your trailing stop at $95.
As the stock price increases, you also need to update your trailing stop. Some trading platforms automatically adjust the trailing stop for you, but on others, you might need to do this manually.
Another important point is to monitor the market and adjust your trailing stop accordingly. Although the trailing stop can adjust automatically, manually monitoring and adjusting it can help you optimize your profits and minimize risk more effectively.
Finally, remember that no tool is perfect. A trailing stop can help limit your risk, but it can’t completely eliminate it.
How to Place a Trailing Stop Order in MT4
First, you need to open a trading position – buy or sell – on MT4. After this position is opened, you need to right-click on it in the ‘Terminal’ tab at the bottom of the MT4 window.
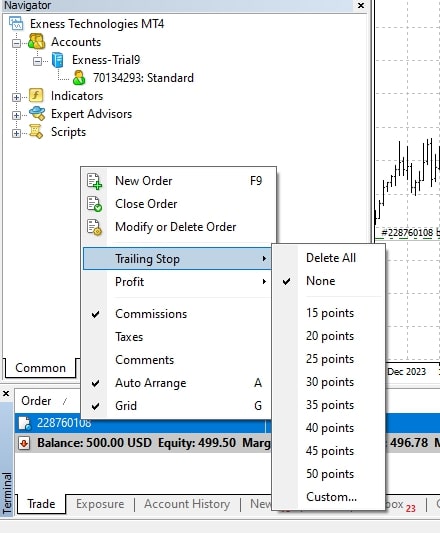
In the menu that appears, you will see the option ‘Trailing Stop’. From there, you can choose the distance for your trailing stop, typically defined in points (each point is equivalent to a pip in Forex). For instance, if you choose 15 points, it means that the trailing stop will be set 15 pips away from the current market price.
An important thing to remember is that the trailing stop in MT4 only works when the MT4 application is open and running. If you close MT4, the trailing stop will also stop functioning. This is different from some other trading platforms where the trailing stop continues to work even when the application is not open.
Setting a trailing stop in MT4 requires an understanding of how this platform works as well as knowledge of trading. It helps you manage risk effectively, especially in volatile markets. However, don’t forget that trailing stops are not always protective against all risks and cannot replace a comprehensive risk management strategy.
The Difference Between Stop Loss and Trailing Stop
Firstly, a stop loss is an order that you place at a certain price level to limit losses in case the market moves in an undesirable direction. It is a basic risk management tool used by most traders.
Meanwhile, a trailing stop is also a type of stop loss, but with a special feature: the ability to adjust itself. A trailing stop moves along with the market price when it moves in the direction of your profit. This means that the trailing stop increases when the price increases but does not decrease when the price falls. It helps you protect the profits you have gained while still maintaining the ability to limit risks.
For example, if you buy a stock at $100 and set a stop loss at $90, the sell order will be triggered if the price falls to $90. However, if you use a trailing stop with a 10-dollar distance, and the stock price rises to $120, the trailing stop will automatically adjust to $110. If the price then falls, the sell order will be triggered at $110, helping you protect most of your profits.
Therefore, the main difference between stop loss and trailing stop lies in the self-adjusting capability of the trailing stop, allowing for more flexible optimization of profits and risk limitation.
Considerations When Using Trailing Stops
When using trailing stops, there are important considerations to keep in mind if you want to maximize the use of this tool in trading. First and foremost, it’s crucial to understand that trailing stops are not a perfect tool. In highly volatile markets, prices can change quickly, and your trailing stop may be triggered unexpectedly, resulting in a sale at a lower price than anticipated.
Another point to note is that trailing stops are only effective when the market moves in the direction of your profit. If the market moves in the opposite direction, the trailing stop will not change, and you will face the same risk of loss as a regular stop loss. Therefore, you should not overly rely on trailing stops; you still need an overall risk management strategy.
Additionally, setting the distance for the trailing stop also requires careful consideration. A distance too small may trigger the sell order too early, while too large a distance may not be effective in protecting profits. It depends on market volatility and your trading style.
Finally, remember that trailing stops require the trading software to be operational to adjust. If you are offline and the software is not running, the trailing stop will not update. Therefore, it may not always be the best option for investors who cannot monitor the market regularly.
Conclusion
Whether you are a beginner or experienced, effectively applying trailing stops can help you maximize profits and minimize risks in trading. Remember, no method is perfect and no tool can make decisions for you. Therefore, combine trailing stops with market knowledge and your personal risk management strategy to achieve the best results. Wishing you success and safety in the financial market!